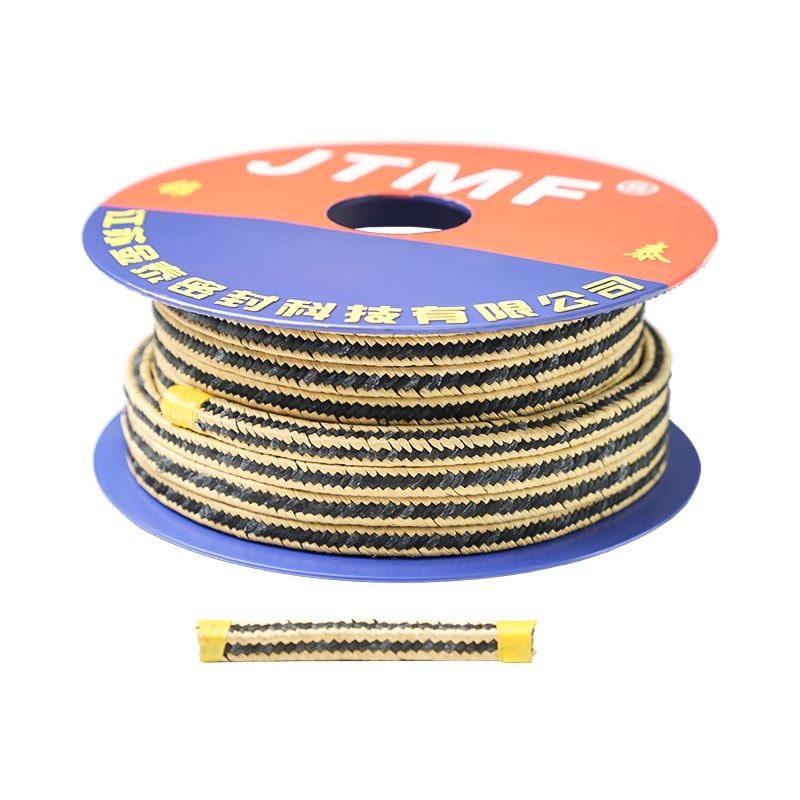
Graphite gland packing temperature range
 2024.12.12
2024.12.12
 Industry News
Industry News
Graphite gland packing is known for its excellent temperature resistance, which is one of the reasons it's widely used in sealing applications in high-temperature environments. The typical temperature range for graphite gland packing depends on its specific formulation and the type of graphite used, but here are general guidelines:
Temperature Range of Graphite Gland Packing:
Continuous Service Temperature:
Graphite packing can typically withstand continuous temperatures ranging from -200°C to +450°C (-328°F to +842°F). This makes it suitable for most high-temperature applications in industries like power generation, petrochemical, and chemical processing.
Intermittent Service Temperature:
In intermittent or short-duration exposure, graphite packing can handle even higher temperatures, up to +600°C to +650°C (+1112°F to +1202°F).
Key Factors Affecting Temperature Limits:
Type of Graphite:
Flexible graphite (expanded graphite) is particularly resistant to high temperatures, whereas other forms of graphite, like carbon fiber composites, may have slightly lower temperature limits.
Conditioning or Lubricants:
Some graphite packings are treated with lubricants or impregnated with other materials (like PTFE, or asbestos in older formulations) to improve performance, which may slightly alter their maximum temperature tolerance.
Atmosphere:
In an inert atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or vacuum), graphite packing can withstand even higher temperatures. However, in an oxidizing environment, the temperature limit can be lower (around 450°C or 842°F), since graphite oxidizes at high temperatures in the presence of oxygen.
Graphite gland packing is capable of handling a broad range of temperatures, typically from -200°C to +450°C (-328°F to +842°F), and can sometimes tolerate even higher temperatures in short-term exposure or controlled conditions. This makes it an ideal choice for sealing in extreme temperature environments.


 Eng
Eng  русский
русский